How are Virus Different From Bacteria Apex: Unveiling 6 Crucial Contrasts for Vibrant Positive Health
Bacteria and viruses are all around us, existing as microscopic entities that play significant roles in the world. While both are classified as microorganisms and can cause diseases. But How are Virus Different From Bacteria Apex, there are fundamental differences in their characteristics, structure, reproduction, and their effects on the human body. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. In this article, we will explore how are Virus different from Bacteria Apex, shedding light on their unique properties and the impact they have on our health.
What are Bacteria?
Bacteria, the oldest known life forms on Earth, are single-celled organisms belonging to the prokaryote domain. They are found in various environments, including soil, water, and the human body. Bacteria communicate and cooperate through complex signaling systems, allowing them to thrive in diverse ecological niches.
Communication is Key
Bacteria possess intricate communication systems known as quorum sensing, which enable them to coordinate group behaviors. This social interaction allows bacteria to function collectively, forming complex communities called biofilms. Through quorum sensing, bacteria can regulate gene expression, toxin production, and the formation of protective barriers.
What are Viruses?
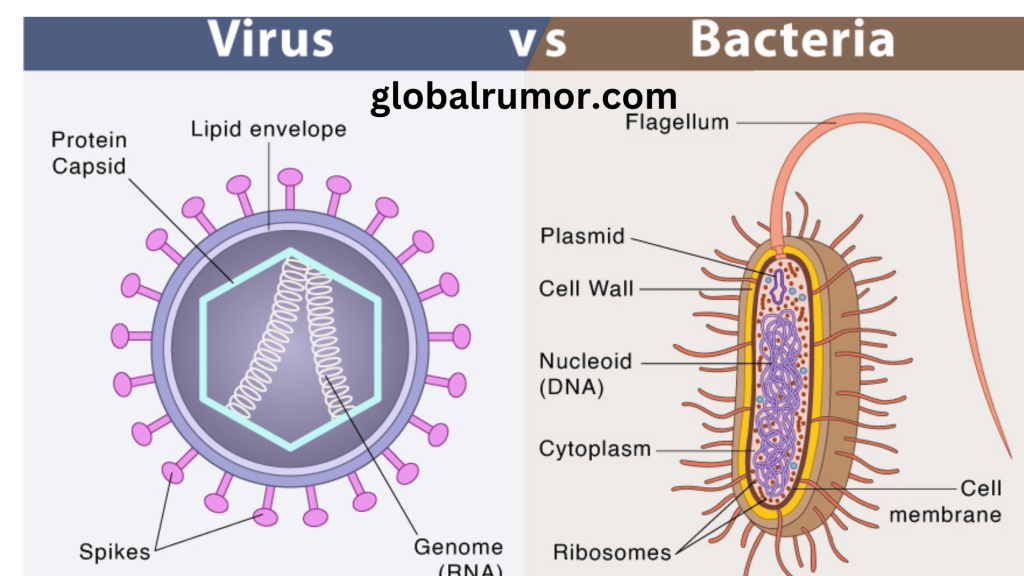
Viruses, on the other hand, are tiny infectious agents that require a host organism to reproduce. Unlike bacteria, viruses lack cellular structures and are considered acellular entities. They consist of genetic material, either DNA or RNA, enclosed within a protein coat called a capsid. Some viruses also have an outer lipid envelope derived from the host cell’s membrane. In short if they are outside of the host they live in a bubble and do not interact with the outer environment unless they find a suitable host for proliferation.
How are Virus Different from Bacteria Apex
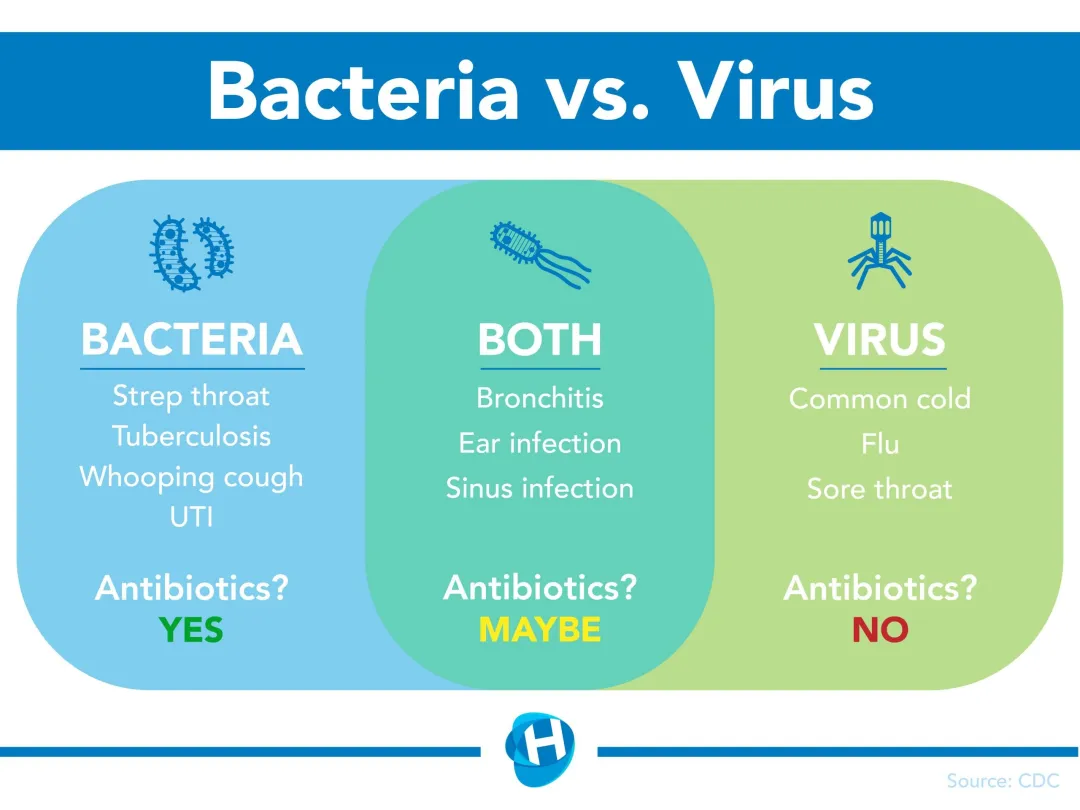
Distinguishing between bacteria and viruses is essential because their treatments differ significantly. Antibiotics, such as penicillin and erythromycin, are effective against bacteria, but they have no impact on viruses. Conversely, antiviral medications like oseltamivir and acyclovir specifically target viral infections. Misusing antibiotics against viral infections can contribute to the rise of antibiotic resistance, a pressing global health concern.
Taking Advantage of these Molecular Powerhouses
Bacteria and viruses have unique properties that scientists harness for various purposes. Bacteria serve as valuable tools in molecular biology and genetic engineering. They can be engineered to produce proteins, enzymes, and other molecules with biomedical and industrial applications. Viruses, on the other hand, have been modified to deliver therapeutic genes in gene therapy and to develop vaccines against viral diseases.
Bacterial and Viral Infections are Often Related
While bacteria and viruses differ in structure and mode of reproduction, bacterial and viral infections often occur simultaneously or sequentially. Bacterial infections can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to viral infections. In some cases, viral infections can pave the way for secondary bacterial infections, as the weakened immune system provides an opportunity for bacteria to proliferate.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the how are virus different from Bacteria Apex, let’s delve deeper into the contrasting characteristics and mechanisms that define them.
Bacteria: Versatile Microorganisms
Bacteria are diverse and adapt to various environments, demonstrating incredible versatility. They can be classified into two major groups: gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, distinguished by their cell wall structure. Gram-positive bacteria have a thick cell wall composed of peptidoglycan, while gram-negative bacteria possess a thinner cell wall and an additional outer membrane.
You may also like to read,
Bacteria reproduce asexually through a process called binary fission, where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. This rapid replication contributes to the high growth rate and adaptability of bacteria. Some bacteria can also exchange genetic material through processes like conjugation, transformation, and transduction, allowing them to acquire new traits and develop antibiotic resistance.
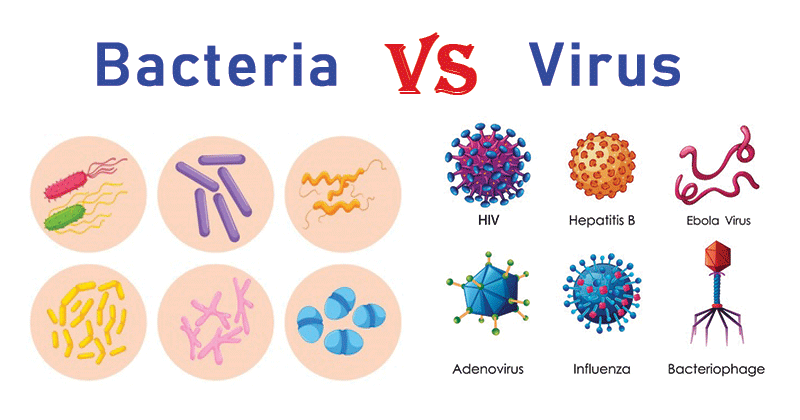
Bacterial infections can cause a range of diseases, such as skin and skin structure infections, pneumonia, gastrointestinal infections, and urinary tract infections. These infections are often treated with antibiotics, which either inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, or disrupt essential metabolic pathways, ultimately killing the bacteria. These microorganisms are found everywhere in the world from the jungles of Amazon to the hottest places in the world. They have a excellent ability to survive in such conditions.
Viruses: Intracellular Hijackers
Viruses are essentially genetic material wrapped in a protein coat. They lack the machinery necessary for independent reproduction and must infect host cells to replicate. Viral infections occur when a virus enters a host organism and injects its genetic material into the host’s cells. Once inside, the viral genetic material hijacks the host cell’s machinery to produce new viral components. Here is the video tutorial explianing how are Virus different from Bacteria Apex.
The replicated viral components assemble into complete viruses, which then burst out of the host cell, destroying it in the process. This cycle of infection and replication continues, leading to the spread of the virus throughout the body. Common viral infections include influenza, the common cold, herpes, and viral pneumonia.
Viral infections can also be prevented through vaccination. Vaccines stimulate the immune system to recognize and mount a defense against specific viruses, providing immunity without the risk of developing the disease itself. Vaccination has been pivotal in the control and eradication of diseases like polio, measles, and smallpox.
FAQs About How are Virus Different From Bacteria Apex
- Can antibiotics treat viral infections? No, antibiotics are only effective against bacterial infections and have no impact on viruses.
- What is the difference between bacteria and viruses in terms of structure?
- Bacteria are single-celled organisms with complex cellular structures, while viruses lack cellular structures and consist of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat.
- Are bacteria and viruses related? Bacteria and viruses are both microorganisms but differ significantly in structure, reproduction, and effects on the human body.
- How do bacteria and viruses cause diseases? Bacteria and viruses can cause diseases by infecting host cells, damaging tissues, and triggering immune responses.
- What role do antibiotics play in treating bacterial infections? Antibiotics target specific cellular processes in bacteria, inhibiting their growth and ultimately killing them.
- Can viral infections be prevented? Yes, vaccination is a highly effective method for preventing viral infections and the spread of viral diseases.
Conclusion
How are Virus different from Bacteria Apex ,bacteria and viruses may be microscopic, but their impact on our health and the world around us is immense. Understanding the differences between these two types of microorganisms is crucial for effective treatment and prevention strategies. While bacteria are versatile organisms capable of independent growth and reproduction, viruses rely on host cells to replicate. By leveraging our knowledge of these molecular powerhouses, we can develop targeted treatments, vaccines, and interventions to combat bacterial and viral infections, ultimately promoting the health and well-being of individuals and populations alike.